
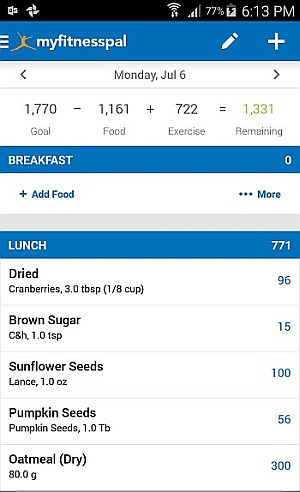
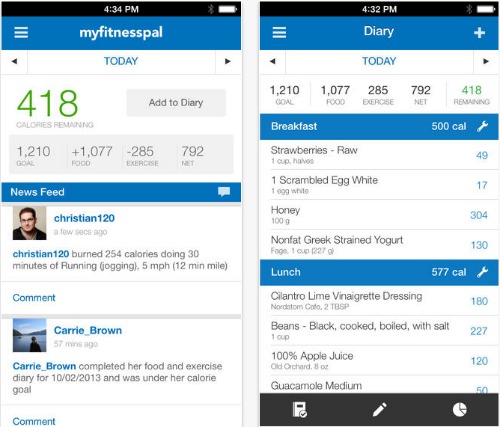
Some of the more commonly used equations for estimating BMR include the Mifflin St-Jeor Equation, Harris-Benedict equation, and Katch-McArdle Formula. This includes physical characteristics such as age, gender, height, and weight. The calculation usually begins with an estimation of basal metabolic rate (BMR), which is based on the use of equations that have been developed for this specific purpose. TDEE is calculated based on the factors described above. Protein, for example, has a far larger thermic effect than dietary fat, since it is more difficult to process. It is sometimes estimated as 10% of food energy intake, but this can vary significantly depending on the type of food consumed. The thermic effect of food, also referred to as specific dynamic action, is the amount of energy required by the body to process and use food. These factors are more specifically referred to as the thermic effect of activity, and non-exercise activity thermogenesis (energy expended for non-sleeping, eating, or sports-like exercise). This includes deliberate exercise as well as other activities that a person may undergo as part of their job or typical daily activities. In other words, it is the minimum energy needed to maintain a person's vital organs only.Īctivity level is a factor that is based on the amount of activity a person undergoes. More often, it is estimated using factors such as a person's basal metabolic rate (BMR), activity level, and the thermic effect of food.īMR is a person's energy usage rate while at rest in a temperate environment when the digestive system is inactive. TDEE is hard to measure accurately and varies day by day. It is the total energy that a person uses in a day. TDEE stands for total daily energy expenditure.

Related: BMI Calculator | Calorie Calculator | Macro Calculator Very intense exercise: 2+ hours of elevated heart rate activity.



 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
